Photodegradation of Ciprofloxacin, Acetaminophen, and Carbamazepine using g-C3N4-based materials for water treatment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61186/jcc.5.2.6Keywords:
Photocatalyst degradation, Photocatalyst, g-C3N4, Ciprofloxacin, Acetaminophen, CarbamazepineAbstract
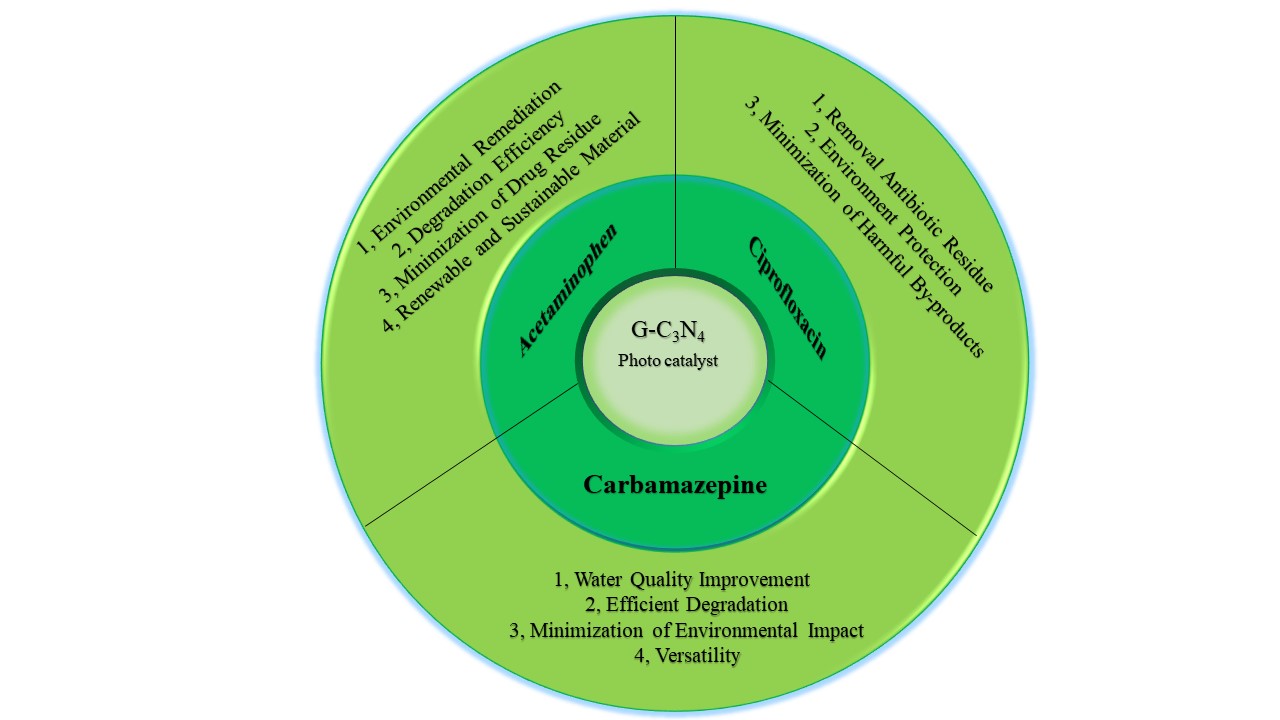
Recently, the use of photocatalytic materials has been suggested as a possible method for cleaning up the environment. A new photocatalyst for enhanced oxidation processes based on radicals is graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4), it is metal-free. g-C3N4 is a trendy two-dimensional (2D) photocatalyst with a number of advantages, such as responsiveness to strong stability, low cost, and visible light. In the present review, the synthesis and characterization of g-C3N4-based photocatalysts are discussed, along with some of their delegate applications in the treatment of wastewater and water (such as acetaminophen, ciprofloxacin, and carbamazepine removal). Meanwhile, the various methods of modification, including doping, defect introduction, heterojunctions, nanocomposites, and so on, are briefly discussed. The associated mechanisms and pertinent discoveries are also examined. Finally, the difficulties, the need for additional study, and the use of g-C3N4-based hybrid membranes are underlined.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 The University of Georgia Publishing House (UGPH)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

