Antibacterial functionalization of dental biomaterials: mechanisms, materials, and emerging Trends
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61882/jcc.7.3.4Abstract
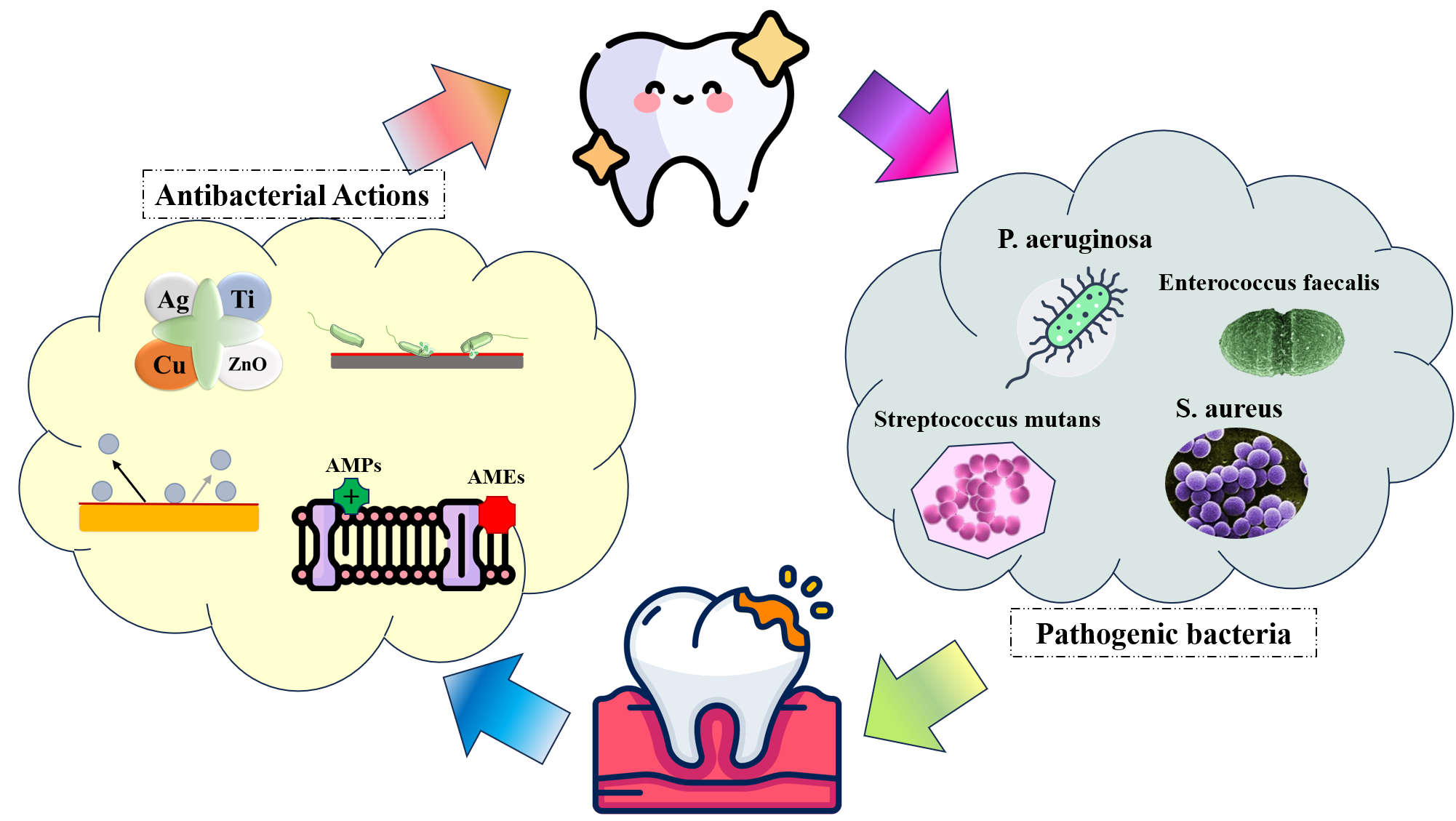
Dental caries, caused by dental plaque and microbial biofilms, is a prevalent disease that poses challenges to the success of prostheses and implants in dentistry. Both inorganic nanomaterials and organic polymeric biomaterials are employed for their antibacterial effects. Nanomaterials, with their high surface-to-volume ratio and diverse shapes, play a crucial role in preventing biofilm formation. Metal nanoparticles such as titanium, silver, copper, and zinc oxide, combined with advanced surface modifications like plasma therapy and coatings, effectively reduce bacterial adhesion and peri-implant inflammation. This review highlights the role of biological and antibacterial materials in managing dental infections and promoting oral health.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 .

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

