Biomedical Applications of Silica Nanoparticle Compounds
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61882/jcc.6.3.5Abstract
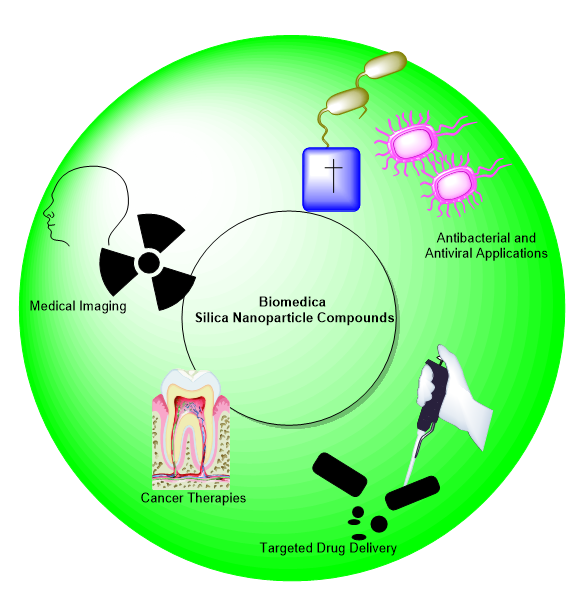
Silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) consist primarily of silicon dioxide and has many qualities, such as selectable particle size, high surface area, and good biocompatibility that make them ideal for additional biomedical usage. SiNPs are becoming increasingly popular amongst researchers for their ability to retain thermal stability and exist in a variety of platforms, such as chromatography, medicine and optics. Advances and growth in the area of nanobiotechnology have alluded to both function and modification of SiNPs through their surface and as structures. One of the most promising uses of SiNPs is the development of therapeutics to target disease like cancer, respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. One of the additional benefits of SiNPs are the ability to also function as carriers of imaging agents, for enhancing medical imaging and imaging modalities like fluorescent imaging, and possibly imagers of the future for early detection of cancer. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) are a subclass of SiNPs, developed to provide controlled drug release with optimal cellular selectivity. What this research highlights are the versatility of SiNPs as applications and devices in modern biomedicine science approaches.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 .

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

