Corrosion Behavior Modeling and Montel Carlo simulation of a Biomedical Ti–Zr–Nb–Ta Alloy for Dental Applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61882/jcc.7.2.5Abstract
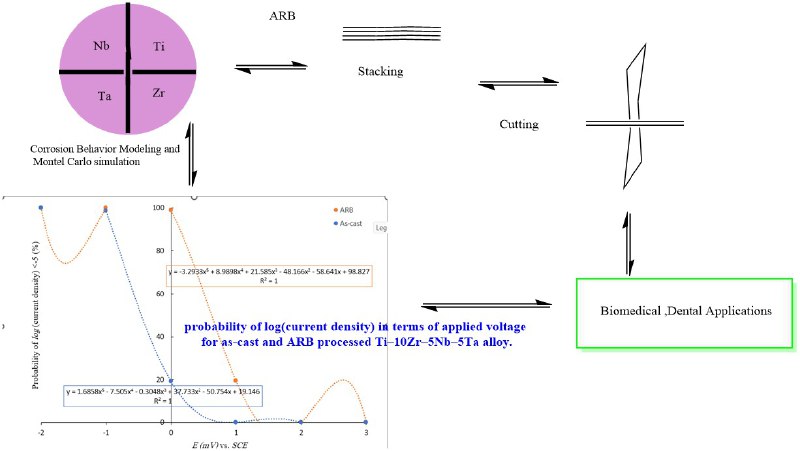
The potentiodynamic polarization behavior of as-cast and accumulative roll-bonded (ARB) Ti–10Zr–5Nb–5Ta alloys was investigated in neutral Ringer solution at 37 °C to assess the influence of microstructural refinement on corrosion resistance and passivation. Using the Tafel equation, the potentiodynamic behavior of the as-cast and ARB-processed alloys was modeled to quantify electrochemical performance, with results indicating that ARB processing significantly modifies passive film characteristics. Model predictions were compared with experimental data, showing good agreement. The models were then coupled with Monte Carlo simulation to account for uncertainties in experimental data and fitting parameters, enabling probabilistic predictions of corrosion behavior. This integrated approach provides a robust evaluation of variability and reliability in electrochemical performance, offering a comprehensive assessment of the alloy’s stability in physiological environments. The findings demonstrate that ARB processing can enhance corrosion resistance, supporting its potential for the development of durable titanium-based biomaterials for demanding biomedical and dental applications.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 .

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

