Development of heavy metal passivators in residue fluid catalytic cracking process
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52547/jcc.4.4.3Keywords:
RFCC, Heavy Metal, Vanadium, Nickel, Metal Trap, Metal PassivatorAbstract
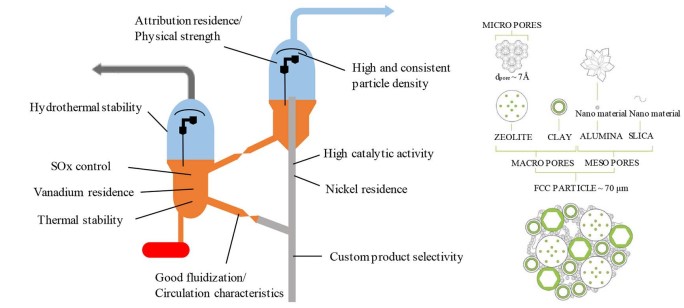
The advancement of residual fluid catalytic cracking (RFCC) is significantly influenced by the development of heavy metals passivation technology. Resids often include larger concentrations of heavy metals (Ni, V, and Fe) than gas oils, primarily in the form of porphyrin complexes and salts of organic acids. Under cracking conditions, metals, especially Ni and V in residues and gas oil deposit on the cracking catalyst and induce adverse dehydrogenation reactions. The catalyst's zeolite component is destroyed by these metals. While reducing the yield of gasoline, active metals increase the yields of coke and hydrogen. Because most cracking FCC units can only tolerate limited amounts of coke and hydrogen, the level of heavy metals on the catalyst needs to be kept under control in order to achieve maximum productivity and profit. Metal passivation enhances catalytic activity and/or selectivity to more desired products by minimizing the detrimental effects of contaminating metals. In this study, we will review heavy metals deactivation mechanism in RFCC process and the potential technological solutions to the catalyst deactivation concern.
References
R. Sadeghbeigi, Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook: An Expert Guide to the Practical Operation, Design, and Optimization of FCC Units, 4 ed., Elsevier Science, England, 2020.
R.H. Harding, A.W. Peters, J.R.D. Nee, New developments in FCC catalyst technology, Applied Catalysis A: General 221(1) (2001) 389-396.
C. Perego, R. Millini, Porous materials in catalysis: challenges for mesoporous materials, Chemical Society Reviews 42(9) (2013) 3956-3976.
A. Akah, M. Al-Ghrami, Maximizing propylene production via FCC technology, Applied Petrochemical Research 5(4) (2015) 377-392.
B. Siddiqui, A.M. Aitani, M.R. Saeed, S. Al-Khattaf, Enhancing the production of light olefins by catalytic cracking of FCC naphtha over mesoporous ZSM-5 catalyst, Topics in Catalysis 53(19) (2010) 1387-1393.
J.S. Buchanan, The chemistry of olefins production by ZSM-5 addition to catalytic cracking units, Catalysis Today 55(3) (2000) 207-212.
A.W. Chester, Chapter 6 CO combustion promoters: past and present, in: M.L. Ocelli (Ed.), Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, Elsevier2007, pp. 67-77.
F. Güleç, W. Meredith, C.E. Snape, Progress in the CO2 Capture Technologies for Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Units—A Review, 8 (2020).
M. Falco, E. Morgado, N. Amadeo, U. Sedran, Accessibility in alumina matrices of FCC catalysts, Applied Catalysis A: General 315 (2006) 29-34.
W. Chen, D. Han, X. Sun, C. Li, Studies on the preliminary cracking of heavy oils: Contributions of various factors, Fuel 106 (2013) 498-504.
F.V. Pinto, A.S. Escobar, B.G. de Oliveira, Y.L. Lam, H.S. Cerqueira, B. Louis, J.P. Tessonnier, D.S. Su, M.M. Pereira, The effect of alumina on FCC catalyst in the presence of nickel and vanadium, Applied Catalysis A: General 388(1) (2010) 15-21.
G.M. Woltermann, J.S. Magee, S.D. Griffith, Chapter 4 Commercial Preparation and Characterization of FCC Catalysts, in: J.S. Magee, M.M. Mitchell (Eds.), Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, Elsevier1993, pp. 105-144.
P.B. Venuto, T. Habib, Catalyst-Feedstock-Engineering Interactions in Fluid Catalytic Cracking, Catalysis Reviews 18(1) (1978) 1-150.
H. Pavol, FCC catalyst-Key element in refinery technology, 2011.
J.R.D. Nee, R.H. Harding, G. Yaluris, W.C. Cheng, X. Zhao, T.J. Dougan, J.R. Riley, Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC), Catalysts and Additives, Kirk?Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology2004.
J.S.J. Hargreaves, A.L. Munnoch, A survey of the influence of binders in zeolite catalysis, Catalysis Science & Technology 3(5) (2013) 1165-1171.
O.A. Topete, Worldwide FCC Equilibrium Catalyst Trends, (2011).
A.W. Chester, Studies on the metal poisoning and metal resistance of zeolitic cracking catalysts, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 26(5) (1987) 863-869.
A. Doyle, A. Saavedra, M.L.B. Tristão, R.Q. Aucelio, Determination of S, Ca, Fe, Ni and V in crude oil by energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry using direct sampling on paper substrate, Fuel 162 (2015) 39-46.
G. Jiménez-García, H.d. Lasa, R. Quintana-Solórzano, R. Maya-Yescas, Catalyst activity decay due to pore blockage during catalytic cracking of hydrocarbons, Fuel 110 (2013) 89-98.
U.J. Etim, B. Xu, R. Ullah, Z. Yan, Effect of vanadium contamination on the framework and micropore structure of ultra stable Y-zeolite, Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 463 (2016) 188-198.
P. Bai, U.J. Etim, Z. Yan, S. Mintova, Z. Zhang, Z. Zhong, X. Gao, Fluid catalytic cracking technology: current status and recent discoveries on catalyst contamination, Catalysis Reviews 61(3) (2019) 333-405.
H.S. Cerqueira, G. Caeiro, L. Costa, F. Ramôa Ribeiro, Deactivation of FCC catalysts, Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical 292(1) (2008) 1-13.
D.J. Rawlence, K. Gosling, Irreversible deactivation of fcc catalysts, Catalysis Today 11(1) (1991) 47-59.
R.F. Wormsbecher, W.-C. Cheng, G. Kim, R.H. Harding, Vanadium Mobility in Fluid Catalytic Cracking, Deactivation and Testing of Hydrocarbon-Processing Catalysts, American Chemical Society1996, pp. 283-295.
W. Letzsch, Fluid catalytic cracking (FCC), in: D.S.J.S. Jones, P.R. Pujadó (Eds.), Handbook of Petroleum Processing, Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, 2006, pp. 239-286.
J.G. Reynolds, NICKEL IN PETROLEUM REFINING, Petroleum Science and Technology 19(7-8) (2001) 979-1007.
O. Bayraktar, Effect of pretreatment on the performance of metal contaminated commercial FCC catalyst, West Virginia University2001.
F.S. Zrinscak Sr, G.G. Karsner, Catalytic cracking of metal-contaminated oils, Google Patents, 1979.
O. Bayraktar, E.L. Kugler, Visualization of the Equilibrium FCC Catalyst Surface by AFM and SEM–EDS, Catalysis Letters 90(3) (2003) 155-160.
D.R. Rainer, E. Rautiainen, B. Nelissen, P. Imhof, C. Vadovic, Simulating iron-induced FCC accessibility losses in lab-scale deactivation, in: M. Occelli (Ed.), Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, Elsevier2004, pp. 165-176.
G. Yaluris, W.C. Cheng, M. Peters, L.T. McDowell, L. Hunt, Mechanism of fluid cracking catalysts deactivation by Fe, in: M. Occelli (Ed.), Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, Elsevier2004, pp. 139-163.
Y. Mathieu, A. Corma, M. Echard, M. Bories, Single and combined Fluidized Catalytic Cracking (FCC) catalyst deactivation by iron and calcium metal–organic contaminants, Applied Catalysis A: General 469 (2014) 451-465.
Z. Liu, Z. Zhang, P. Liu, J. Zhai, C. Yang, Iron Contamination Mechanism and Reaction Performance Research on FCC Catalyst, Journal of Nanotechnology 2015 (2015) 273859.
Z. Yuxia, D. Quansheng, L. Wei, T. Liwen, L. Jun, Chapter 13 Studies of iron effects on FCC catalysts, in: M.L. Ocelli (Ed.), Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, Elsevier2007, pp. 201-212.
F. Güleç, W. Meredith, C.-G. Sun, C.E. Snape, Demonstrating the applicability of chemical looping combustion for the regeneration of fluid catalytic cracking catalysts, Chemical Engineering Journal 389 (2020) 124492.
F. Güleç, W. Meredith, C.-G. Sun, C.E. Snape, A novel approach to CO2 capture in Fluid Catalytic Cracking—Chemical Looping Combustion, Fuel 244 (2019) 140-150.
F. Güleç, W. Meredith, C.-G. Sun, C.E. Snape, Selective low temperature chemical looping combustion of higher alkanes with Cu- and Mn- oxides, Energy 173 (2019) 658-666.
R.H. Nielsen, P.K. Doolin, Chapter 10 Metals Passivation, in: J.S. Magee, M.M. Mitchell (Eds.), Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, Elsevier1993, pp. 339-384.
M.W. Anderson, M.L. Occelli, S.L. Suib, Luminescence probes of vanadium-contaminated fluid cracking catalysts, Journal of Catalysis 118(1) (1989) 31-42.
W.P. Hettinger Jr, H.W. Beck, E.B. Cornelius, P.K. Doolin, R.A. Kmecak, S.M. Kovach, Residuos en las unidades de FCC, Oilgas 18(212) (1985) 68-76.
D.F. Tatterson, R.L. Mieville, Nickel/vanadium interactions on cracking catalyst, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 27(9) (1988) 1595-1599.
R.F. Wormsbecher, A.W. Peters, J.M. Maselli, Vanadium poisoning of cracking catalysts: Mechanism of poisoning and design of vanadium tolerant catalyst system, Journal of Catalysis 100(1) (1986) 130-137.
G.L. Woolery, A.A. Chin, G.W. Kirker, A. Huss Jr, X-ray absorption study of vanadium in FCC catalysts, American Chemical Society, Division of Petroleum Chemistry, Preprints;(USA) 32(CONF-8708311-) (1987).
L.A. Pine, P.J. Maher, W.A. Wachter, Prediction of cracking catalyst behavior by a zeolite unit cell size model, Journal of Catalysis 85(2) (1984) 466-476.
R.D.M. Pimenta, M.M. Pereira, U.d. Nascimento, J. Gorne, E. Bernadete, L.Y. Lau, Effect of vanadium contamination on H-ZSM-5 zeolite deactivation, Catalysis Today 133-135 (2008) 805-808.
D.V. Cristiano-Torres, Y. Osorio-Pérez, L.A. Palomeque-Forero, L.E. Sandoval-Díaz, C.A. Trujillo, The action of vanadium over Y zeolite in oxidant and dry atmosphere, Applied Catalysis A: General 346(1) (2008) 104-111.
L.-E. Sandoval-Díaz, J.-M. Martínez-Gil, C.A. Trujillo, The combined effect of sodium and vanadium contamination upon the catalytic performance of USY zeolite in the cracking of n-butane: Evidence of path-dependent behavior in Constable–Cremer plots, Journal of Catalysis 294 (2012) 89-98.
P.K. Doolin, J.F. Hoffman, M.M. Mitchell, Role of metal contaminants in the production of carbon dioxide during the regeneration of cracking catalysts, Applied Catalysis 71(2) (1991) 233-246.
V. Cadet, F. Raatz, J. Lynch, C. Marcilly, Nickel contamination of fluidised cracking catalysts: A model study, Applied Catalysis 68(1) (1991) 263-275.
C.H. Bartholomew, R.B. Pannell, J.L. Butler, Support and crystallite size effects in CO hydrogenation on nickel, Journal of Catalysis 65(2) (1980) 335-347.
C.H. Bartholomew, R.J. Farrauto, Chemistry of nickel-alumina catalysts, Journal of Catalysis 45(1) (1976) 41-53.
J.L. Palmer, E.B. Cornelius, Separating equilibrium cracking catalyst into activity graded fractions, Applied Catalysis 35(2) (1987) 217-235.
S.-Q. Yu, H.-P. Tian, Y.-X. Zhu, Z.-Y. Dai, J. Long, Mechanism of Rare Earth Cations on the Stability and Acidity of Y Zeolites, Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica 27(11) (2011) 2528-2534.
Y. Yung, K. Bruno, Low rare earth catalysts for FCC operations, Petroleum technology quarterly 17(1) (2012).
R. Wormsbecher, W. Cheng, D. Wallenstein, Role of the rare earth elements in fluid catalytic cracking, Grace Davison Catalagram 108 (2010) 19.
M.K. Maholland, Improving FCC catalyst performance, Petroleum technology quarterly 11(2) (2006) 41-42.
A. Akah, Application of rare earths in fluid catalytic cracking: A review, Journal of Rare Earths 35(10) (2017) 941-956.
B.H. Davis, M.L. Occelli, Advances in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, catalysts, and catalysis, CRC press2009.
J.S. Magee, M.M. Mitchell, Fluid Catalytic Cracking: Science and Technology, Elsevier Science1993.
H.J. Jeon, S.K. Park, S.I. Woo, Evaluation of vanadium traps occluded in resid fluidized catalytic cracking (RFCC) catalyst for high gasoline yield, Applied Catalysis A: General 306 (2006) 1-7.
D. Wallenstein, K. Schäfer, R.H. Harding, Impact of rare earth concentration and matrix modification in FCC catalysts on their catalytic performance in a wide array of operational parameters, Applied Catalysis A: General 502 (2015) 27-41.
J.G. Nery, Y.P. Mascarenhas, T.J. Bonagamba, N.C. Mello, E.F. Souza-Aguiar, Location of cerium and lanthanum cations in CeNaY and LaNaY after calcination, Zeolites 18(1) (1997) 44-49.
C.R. Moreira, N. Homs, J.L.G. Fierro, M.M. Pereira, P. Ramírez de la Piscina, HUSY zeolite modified by lanthanum: Effect of lanthanum introduction as a vanadium trap, Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 133(1) (2010) 75-81.
C.R. Moreira, M.H. Herbst, P.R. de la Piscina, J.-L.G. Fierro, N. Homs, M.M. Pereira, Evidence of multi-component interaction in a V–Ce–HUSY catalyst: Is the cerium–EFAL interaction the key of vanadium trapping?, Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 115(3) (2008) 253-260.
C.R. Moreira, M.M. Pereira, X. Alcobé, N. Homs, J. Llorca, J.L.G. Fierro, P. Ramírez de la Piscina, Nature and location of cerium in Ce-loaded Y zeolites as revealed by HRTEM and spectroscopic techniques, Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 100(1) (2007) 276-286.
T.J. Dougan, U. Alkemade, B. Lakhanpal, L.T. Boock, New vanadium trap proven in commercial trials, Oil and Gas Journal;(United States) 92(39) (1994).
W. Huai-Ping, W. Fang-Zhu, W. Wen-Ru, Effect of vanadium poisoning and vanadium passivation on the structure and properties of rehy zeolite and FCC catalyst, ACS Fuels 45 (2000) 623.
B.a. Fe´ron, P. Gallezot, M. Bourgogne, Hydrothermal aging of cracking catalysts: V. Vanadium passivation by rare-earth compounds soluble in the feedstock, Journal of Catalysis 134(2) (1992) 469-478.
T. Myrstad, Effect of vanadium on octane numbers in FCC-naphtha, Applied Catalysis A: General 155(1) (1997) 87-98.
P.H. Kasai, Zeolite Chemistry and Catakysis, ACS Monograph 171 350 (1976).
X. Du, H. Zhang, G. Cao, L. Wang, C. Zhang, X. Gao, Effects of La2O3, CeO2 and LaPO4 introduction on vanadium tolerance of USY zeolites, Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 206 (2015) 17-22.
U.J. Etim, P. Bai, R. Ullah, F. Subhan, Z. Yan, Vanadium contamination of FCC catalyst: Understanding the destruction and passivation mechanisms, Applied Catalysis A: General 555 (2018) 108-117.
X. Pang, S. Sun, W. Ding, Study on nickel-tolerant matrix for FCC catalysts, Ind. Catal 10 (2002) 50-53.
Y. Shi, High metal tolerance matrix for FCC catalyst, Pet. Process. Petrochem 27 (1996) 37-40.
C. Yuan, Z. Pan, Z. Tan, H. Zhang, Synthesis of ordered mesoporous alumina and its application in preparation of heavy metal tolerance FCC catalyst, Pet. Process. Petrochem 48 (2017) 52-55.
C. Yuan, L. Zhou, Q. Chen, C. Su, Z. Li, G. Ju, The Research on Anti-Nickel Contamination Mechanism and Performance for Boron-Modified FCC Catalyst, Materials 15(20) (2022) 7220.
W.S. Letzsch, L.L. Upson, A.G. Ashton, Passivate nickel in FCC feeds, Hydrocarbon processing (International ed.) 70(6) (1991) 89-92.
S. Oruji, R. Khoshbin, R. Karimzadeh, Combination of precipitation and ultrasound irradiation methods for preparation of lanthanum-modified Y zeolite nano-catalysts used in catalytic cracking of bulky hydrocarbons, Materials Chemistry and Physics 230 (2019) 131-144.
M.A.A. Majed, C.T. Tye, Catalytic cracking of used vegetable oil to green fuel with metal functionalized ZSM-5 Catalysts, Malaysian Journal of Analytical Science 22(1) (2018) 9.
O. Alfernando, S. Fitri, Used cooking oil catalytic cracking using Cr-charcoal ion-exchanged catalyst, IOP Publishing, p. 022031.
G.L. Baugis, H.F. Brito, W. de Oliveira, F. Rabello de Castro, E.F. Sousa-Aguiar, The luminescent behavior of the steamed EuY zeolite incorporated with vanadium and rare earth passivators, Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 49(1) (2001) 179-187.
P. Liu, Y. Cui, G. Gong, X. Du, J. Wang, X. Gao, M. Jia, J. Yu, Vanadium contamination on the stability of zeolite USY and efficient passivation by La2O3 for cracking of residue oil, Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 279 (2019) 345-351.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2022 The University of Georgia Publishing House (UGPH)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors will be asked, upon acceptance of an article, to transfer copyright of the article to the Publisher. This will ensure the widest possible dissemination of information under copyright laws. The submitted materials may be considered for inclusion but can not be returned.
Licensing: The JCC articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source (appropriate citation), provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
*Author rights
As an author you (or your employer or institution) have certain rights to reuse your work.


